题目:合并两个有序数组
难度:Easy
题目描述:
题目
给你两个有序整数数组 nums1 和 nums2,请你将 nums2 合并到 nums1 中,使 nums1 成为一个有序数组。
说明:
- 初始化 nums1 和 nums2 的元素数量分别为 m 和 n 。
- 你可以假设 nums1 有足够的空间(空间大小大于或等于 m + n)来保存 nums2 中的元素。
示例:
输入:
nums1 = [1,2,3,0,0,0], m = 3
nums2 = [2,5,6], n = 3 输出:
[1,2,2,3,5,6]
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-sorted-array
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
解题思路
方法一:合并后排序
直觉
最朴素的解法就是将两个数组合并之后再排序。
该算法只需要一行(Java是2行),时间复杂度较差,为O((n + m)log(n + m))。这是由于这种方法没有利用两个数组本身已经有序这一点。
实现
Python版
class Solution:
def merge(self, nums1: List[int], m: int, nums2: List[int], n: int) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify nums1 in-place instead.
"""
nums1[:] = sorted(nums1[:m] + nums2)Java版
class Solution {
public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
System.arraycopy(nums2, 0, nums1, m, n);
Arrays.sort(nums1);
}
}Scala版
object Solution {
def merge(nums1: Array[Int], m: Int, nums2: Array[Int], n: Int): Unit = {
}
}复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度 : O((n+m)log(n+m))
- 空间复杂度 : O(1)
方法二:双指针 / 从前往后
直觉
一般而言,对于有序数组可以通过双指针法达到O(n+m)的时间复杂度。
最直接的算法实现是将指针p1 置为 nums1的开头, p2为 nums2的开头,在每一步将最小值放入输出数组中。
由于 nums1 是用于输出的数组,需要将nums1中的前m个元素放在其他地方,也就需要O(m) 的空间复杂度。
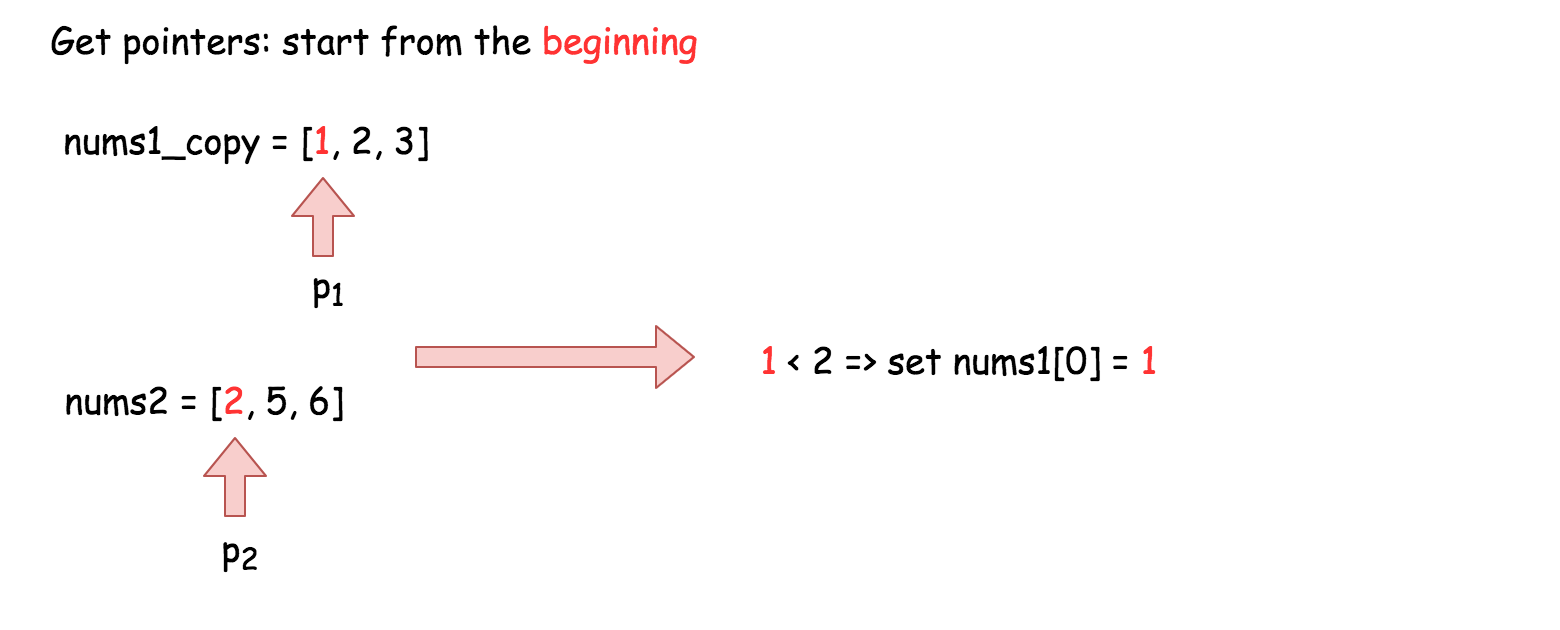
实现
Python版
class Solution(object):
def merge(self, nums1, m, nums2, n):
"""
:type nums1: List[int]
:type m: int
:type nums2: List[int]
:type n: int
:rtype: void Do not return anything, modify nums1 in-place instead.
"""
# Make a copy of nums1.
nums1_copy = nums1[:m]
nums1[:] = []
# Two get pointers for nums1_copy and nums2.
p1 = 0
p2 = 0
# Compare elements from nums1_copy and nums2
# and add the smallest one into nums1.
while p1 < m and p2 < n:
if nums1_copy[p1] < nums2[p2]:
nums1.append(nums1_copy[p1])
p1 += 1
else:
nums1.append(nums2[p2])
p2 += 1
# if there are still elements to add
if p1 < m:
nums1[p1 + p2:] = nums1_copy[p1:]
if p2 < n:
nums1[p1 + p2:] = nums2[p2:]复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度 : O(n + m)
- 空间复杂度 : O(m)
方法三 : 双指针 / 从后往前
直觉
方法二已经取得了最优的时间复杂度O(n + m),但需要使用额外空间。这是由于在从头改变nums1的值时,需要把nums1中的元素存放在其他位置。
如果我们从结尾开始改写 nums1 的值又会如何呢?这里没有信息,因此不需要额外空间。
这里的指针 p 用于追踪添加元素的位置。


实现
Python版
class Solution(object):
def merge(self, nums1, m, nums2, n):
"""
:type nums1: List[int]
:type m: int
:type nums2: List[int]
:type n: int
:rtype: void Do not return anything, modify nums1 in-place instead.
"""
# two get pointers for nums1 and nums2
p1 = m - 1
p2 = n - 1
# set pointer for nums1
p = m + n - 1
# while there are still elements to compare
while p1 >= 0 and p2 >= 0:
if nums1[p1] < nums2[p2]:
nums1[p] = nums2[p2]
p2 -= 1
else:
nums1[p] = nums1[p1]
p1 -= 1
p -= 1
# add missing elements from nums2
nums1[:p2 + 1] = nums2[:p2 + 1]Java版
class Solution {
public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
// two get pointers for nums1 and nums2
int p1 = m - 1;
int p2 = n - 1;
// set pointer for nums1
int p = m + n - 1;
// while there are still elements to compare
while ((p1 >= 0) && (p2 >= 0))
// compare two elements from nums1 and nums2
// and add the largest one in nums1
nums1[p--] = (nums1[p1] < nums2[p2]) ? nums2[p2--] : nums1[p1--];
// add missing elements from nums2
System.arraycopy(nums2, 0, nums1, 0, p2 + 1);
}
}复杂度
- 时间复杂度 : O(n + m)
- 空间复杂度 : O(1)



